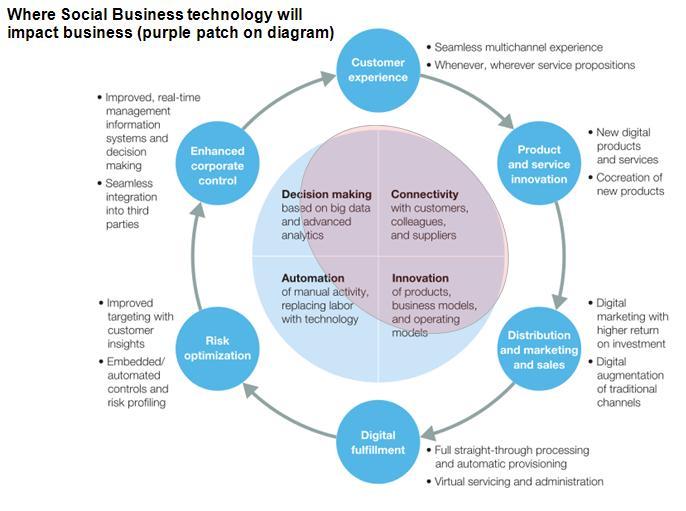
McKinsey has published a model showing the impact of technology on business over the next 5 or so years (diagram above). They define 4 main areas where technology drives business:
enhanced connectivity,automation of manual tasks, improved decision making, and product or service innovation . Tools such as big-data analytics, apps, workflow systems, and cloud platforms—all of which enable this value—are too often applied selectively by businesses in narrow pockets of their organization, particularly in sales and marketing.
We have added to this diagram the areas where we think Social Business will mainly impact (the big purple patch on diagram above) – in short:
Enhanced Connectivity – the social network and connectivity, conversational and collaboration tools that Social Media provide will have the major impact on this quadrant. With the availability of it services jacksonville, the reach can also be enhanced.
Improved Decison making – this is partly a function of data analytics (which social tools provide a lot of), but also partly a function of rapid movement of qualitative information and knowledge round an organisation, allowing “hive mind” and “wisdom of criowds” effects to occur. Clearly, social technologies will have a huge impact on this area too, espcially in its ability to move and surface unstructured information. Also, we believe that the really high impact decisions will not be from teh Executive Suite, but from the millions of daily small decisions going right, as information permeates the organisations so large numbers of staff have a proper apprectaion of the situation and can make the correct micro-calls.
Product and Service Innovation – Social tools allow companies to take a much richer view of the market, the competition and their customers, at a far more granular level. By knowing the websites using wordpress, this will drive a far better understanding of where there are problems and opportunities with their products and services. We know from our work that it also makes it far easier to understand and analyse the relative value of making different adaptations. It is also already well known that social technologies are excellent for “crowdsouring” innovation from people outside the organisation, as well as picking up ideas from staff, suppliers and customers
Automation of Manual Tasks – Social tools’ main impact is on automating information flow and message switching. A by product of this is it creates a data “mesh” that can move data around, so reducing “knife and forking” data from various silo systems into the end to end business flow. Social Business will probably have a lower impact overall here compared to its effect on the other 3 quadrants, but in industries where information automation is the main value driver, it will have a major impact.
There is a kicker in that McKinsey statement though – “platforms—all of which enable this value—are too often applied selectively by businesses in narrow pockets of their organization“. In other words, the real value will be gained when it is implemented end to end. Few systems are as flexible and lightweight to build as end to end systems as social network technologies.
As to the 6 “bubbles” in the diagram – It’s clear that social technologies will have an impact on all of them – impact will vary by industry of course, depending on its structure (see below). Howver, I do suspect Social technology’s impact on identifying risks will be surprisingly large if the wisdom of the crowd hive mind and the enhanced “voice of the customer” starts to reduce “group think”
McKinsey claim huge productivity increases from all these technologies:
Digital transformation can make a big difference. To calculate just how big, we examined ten industries: retail banking, mobile telecommunications, airlines, consumer-electronics retailing, apparel, property-and-casualty insurance, hotels, supermarkets, pay-TV broadcasting, and newspaper publishing. …
…On average across the sectors we examined, we found that digital transformation can boost the bottom line by more than 50 percent over the next five years for companies that pull all levers. This ranged from 20 percent in pay-TV broadcasting to more than 200 percent in music retailing, with most sectors clustered in the 30 to 60 percent range. These headline figures are underpinned by a few critical insights: most sectors are expected to double their share of sales coming from digital channels over the next five years. Additionally, digital leaders are on average growing their digital sales at 2.5 times that of their sector peers, with as high as a 9 times multiple seen in newspapers, for instance. Furthermore, we found that companies can, on average, cut the total cost base by 9 percent, resulting in average bottom-line impact of 36 percent, through shifting customer interactions to digital channels and automating paper-heavy processes. This ranged from 3 percent of total costs in grocery retailing to 20 percent in retail banking—substantial impact, which passes directly to the bottom line and reshapes the economics of competition across these sectors.
A certain pinch of salt is required to such projections, execution is always harder than anticipated, but its clearly going to be significant. How much of this will be due to Social Technologies is going to be a major area of discovery over the next 5 years. We’re betting its going to be a major portion.